Ποια είναι τα επίπεδα διόρθωσης Fibonacci;
)
Πίνακας περιεχομένων:
Ποια είναι τα επίπεδα διόρθωσης Fibonacci;
Η ακολουθία Fibonacci και οι αναλογίες της με απλά λόγια
Πώς να υπολογίσετε τις γραμμές διόρθωσης Fibonacci
Ποια είναι τα συνηθισμένα επίπεδα διόρθωσης;
Μέτριες διορθώσεις
Χρυσές διορθώσεις
Περιορισμοί στη χρήση των επιπέδων διόρθωσης Fibonacci
Συμπέρασμα
Συχνές ερωτήσεις (FAQs)
Εάν ασχολείστε με το χρηματιστήριο ή έχετε οποιαδήποτε σχέση με αυτό, είναι σχεδόν βέβαιο ότι έχετε ακούσει για τους αριθμούς Fibonacci. Οι αριθμοί Fibonacci, που πήραν το όνομά τους από τον Λεονάρντο Φιμπονάτσι, σχετίζονται με τη συμμετρία και την αναλογία. Ας ρίξουμε μια ματιά στους αριθμούς Fibonacci, οι οποίοι χρησιμοποιούνται στον προγραμματισμό, τα χρηματοοικονομικά και φυσικά, στις συναλλαγές.
Ποια είναι τα επίπεδα διόρθωσης Fibonacci;
Κάθε επίπεδο διόρθωσης Fibonacci αντιπροσωπεύει ένα ποσοστό προηγούμενης κίνησης της τιμής που έχει ανακληθεί. Οι traders δίνουν ιδιαίτερη προσοχή σε βασικά επίπεδα, όπως τα 23.6%, 38.2%, 61.8%, καθώς και σε ορισμένες περιπτώσεις, στα 76.4% ή 78.6%. Το επίπεδο 50% συχνά συμπεριλαμβάνεται στον χάρτη, παρόλο που δεν αποτελεί επίσημη αναλογία Fibonacci.
Μόλις εντοπίσετε μια σημαντική διακύμανση της τιμής, όπως μια ανοδική ή πτωτική κίνηση, μπορείτε να εφαρμόσετε τις αναλογίες Fibonacci σε αυτό το εύρος. Κάθε επίπεδο στη συνέχεια υποδηλώνει τον βαθμό διόρθωσης της προηγούμενης κίνησης, βασισμένο σε μια αναλογία που εμφανίζεται συχνά στη φύση.
Βασικά σημεία:
- Τα επίπεδα διόρθωσης Fibonacci είναι 23.6%, 38.2%, 61.8% και μερικές φορές τα 76.4%/78.6%, καθώς και το 50%.
- Αυτά τα επίπεδα στοχεύουν στον εντοπισμό πιθανών περιοχών στήριξης ή αντίστασης κατά τη διάρκεια των διορθώσεων.
- Το επίπεδο 61.8% αντιστοιχεί στη διάσημη "χρυσή αναλογία" (Golden Ratio) 1.618, η οποία θεωρείται ιδιαίτερα σημαντική.
- Οι διορθώσεις Fibonacci πρέπει να συνδυάζονται μαζι με άλλα τεχνικά εργαλεία και δεν πρέπει να χρησιμοποιούνται μεμονωμένα.
Η ακολουθία Fibonacci και οι αναλογίες της με απλά λόγια
Μερικές απλές μαθηματικές ιδιότητες της ακολουθίας Fibonacci:
- Φανταστείτε μια αριθμητική ακολουθία που ξεκινά με το ταπεινό 0 και 1 και στη συνέχεια εξελίσσεται σε ένα μαγευτικό μοτίβο, όπου κάθε επόμενος αριθμός προκύπτει από το άθροισμα των δύο προηγούμενων. Αυτός είναι ο συναρπαστικός κόσμος της ακολουθίας Fibonacci.
- Καθώς προχωράτε βαθύτερα στην ακολουθία και διαιρείτε έναν αριθμό Fibonacci με τον αμέσως προηγούμενό του, εμφανίζεται μια συναρπαστική αναλογία που πλησιάζει όλο και περισσότερο το 1.618. Σαν ένας μαθηματικός χορός, αυτή η αναλογία γίνεται όλο και πιο ακριβής καθώς οι αριθμοί μεγαλώνουν.
- Σε μια κοσμική ανατροπή, όταν αντιστρέψετε αυτή τη διαδικασία και διαιρέσετε με τον επόμενο αριθμό, θα συναντήσετε τη μυστηριώδη αναλογία 0.618. Αυτή η φαινομενικά ταπεινή αναλογία αποτελεί τη βάση του επιπέδου διόρθωσης 61.8% - έναν βασικό παράγοντα στον κόσμο του trading.
- Προχωρώντας ακόμη βαθύτερα, η διαίρεση ενός αριθμού με εκείνον που βρίσκεται δύο θέσεις μπροστά στην ακολουθία αποκαλύπτει την αναλογία 0.382. Αυτή η αναλογία, με τη σειρά της, δημιουργεί το επίπεδο διόρθωσης 38.2% - έναν καθοδηγητικό φάρο για όσους πλοηγούνται στις αγορές.
- Και τέλος, σαν να κοιτάμε στον ίδιο τον ιστό του σύμπαντος, η διαίρεση με τον αριθμό που βρίσκεται τρεις θέσεις μπροστά αποκαλύπτει τη μυστηριώδη αναλογία 0.236. Αυτός ο φαινομενικά ασήμαντος αριθμός κρατά το κλειδί για το επίπεδο διόρθωσης 23.6%, μια διακριτική αλλά ισχυρή δύναμη στον κόσμο της χρηματοοικονομικής ανάλυσης.
Στην ακολουθία Fibonacci, οι αριθμοί 1.618 και 0.618 είναι γνωστοί ως η αναλογία Fibonacci, ή η "Χρυσή Αναλογία", η οποία συναντάται στη φύση, την τέχνη και τη βιολογία. Αυτή η αναλογία εμφανίζεται σε στοιχεία όπως τα κοχύλια, τα ηλιοτρόπια, οι γαλαξίες και η αρχαία ελληνική αρχιτεκτονική.
Έτσι, ενώ μπορεί να φαίνονται ως καθαρά μαθηματικά, τα ποσοστά διόρθωσης Fibonacci αντανακλούν μοτίβα που επαναλαμβάνονται συνεχώς στον φυσικό κόσμο γύρω μας. Ίσως γι’ αυτό φαίνεται πως επηρεάζουν και τις χρηματοοικονομικές αγορές με έναν αφηρημένο αλλά αξιοσημείωτο τρόπο.
Πώς να υπολογίσετε τις γραμμές διόρθωσης Fibonacci
Για να βρείτε τα επίπεδα διόρθωσης, υπολογίστε τη διαφορά και πολλαπλασιάστε την με 38.2% και 61.8%.
- Αν οι τιμές ανεβαίνουν μετά από πτώση, προσθέστε αυτά τα επίπεδα στη χαμηλότερη τιμή.
- Αν οι τιμές πέφτουν μετά από άνοδο, αφαιρέστε τα από την υψηλότερη τιμή.
Μπορούμε να παρατηρήσουμε ένα ξεκάθαρο παράδειγμα διόρθωσης στις τιμές της μετοχής της Tesla στα επίπεδα 38.2% και 61.8%. Αφού έφτασε σε ιστορικό υψηλό το 2021, η τιμή της μετοχής της Tesla υποχώρησε στο 0.382 της διόρθωσης Fibonacci και στη συνέχεια ανέκαμψε στο 0.618. Επιπλέον, η τιμή σταθεροποιήθηκε σε αυτά τα επίπεδα αρκετές φορές.
)
Ακολουθώντας αυτήν τη λογική, πολλοί traders μπορούν να προσδιορίσουν το σημείο εισόδου ή εξόδου μιας συναλλαγής, να κάνουν προβλέψεις για το πότε η τιμή θα αντιστραφεί και ούτω καθεξής. Φαίνεται σχεδόν σαν οι αριθμοί Fibonacci να ασκούν μια αόρατη βαρυτική έλξη στις τιμές κατά τη διάρκεια αυτής της ασταθούς περιόδου.
Πολλοί traders παρακολουθούν στενά αυτά τα επίπεδα, γεγονός που δημιουργεί στην πράξη ένα αυτοεκπληρούμενο μοτίβο στις αγορές.
Ποια είναι τα συνηθισμένα επίπεδα διόρθωσης;
Μια μικρή διόρθωση στο 23.6% είναι απλώς μια σύντομη παύση, ενώ οι διορθώσεις 38.2% έως 50% είναι μέτριας έντασης. Το επίπεδο 61.8%, που συνδέεται με τη Χρυσή Αναλογία (Golden Ratio), είναι το σημείο όπου συχνά συμβαίνουν οι πιο σημαντικές αλλαγές στην τάση.
Για να χρησιμοποιήσετε αποτελεσματικά αυτά τα επίπεδα, εστιάστε σε ημερήσια διαγράμματα 3 έως 9 μηνών, τα οποία δείχνουν τις μέτριες διορθώσεις 38.2%-50% και την πιο ισχυρή 61.8%.
Συνδυάστε το εργαλείο Fibonacci με άλλους τεχνικούς δείκτες για να επιβεβαιώσετε πιθανές αλλαγές στην τάση.
Μέτριες διορθώσεις
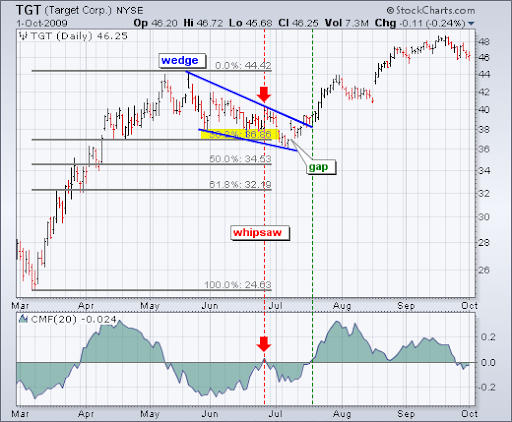
Στο εντυπωσιακό γράφημα της Target (TGT), παρατηρούμε μια διόρθωση 38%, συνοδευόμενη από ένα μοτίβο falling wedge. Αυτός ο συνδυασμός, μαζί με τον δείκτη Chaikin Money Flow, ο οποίος έγινε θετικός, υποδηλώνει μια πιθανή αντιστροφή της τάσης.
Αν και η αρχική προσπάθεια απέτυχε, η TGT βρήκε επιτυχία στα μέσα Ιουλίου, σημειώνοντας ένα gap-up και διασπώντας την καθοδική γραμμή τάσης του wedge.
)
Η PetSmart (PETM) παρουσίασε μια παρόμοια εικόνα, με διόρθωση 38% και ένα προηγούμενο επίπεδο στήριξης στα $28, το οποίο μετατράπηκε σε αντίσταση.
Ο δείκτης Williams %R, που έδειχνε ότι η μετοχή ήταν υπεραγορασμένη, έκανε την ανάλυση ακόμα πιο ενδιαφέρουσα.
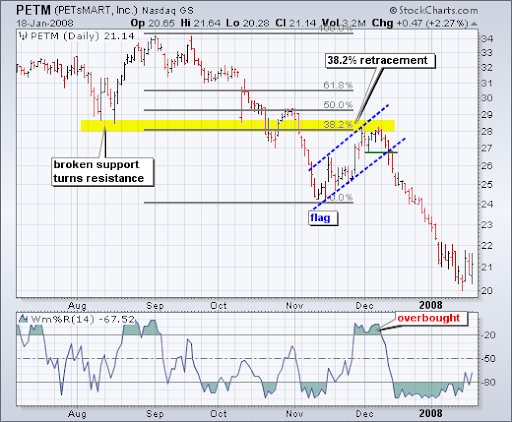)
Η επιβεβαίωση ήρθε όταν ο Williams %R υποχώρησε κάτω από το -20%, ενώ η PETM σχημάτισε ένα μικρό rising flag pattern, το οποίο τελικά διασπάστηκε προς τα κάτω στα μέσα Δεκεμβρίου.
Αυτά τα παραδείγματα δείχνουν ότι ο συνδυασμός των επιπέδων Fibonacci με μοτίβα γραφημάτων και τεχνικούς δείκτες μπορεί να προσφέρει μια πιο καθαρή εικόνα των πιθανών αντιστροφών της αγοράς. Οι αριθμοί Fibonacci φαίνεται να διαθέτουν μια μαγνητική έλξη, καθοδηγώντας τις τιμές κατά τη διάρκεια διορθώσεων και ανακάμψεων στην αγορά.
Τα γραφήματα των TGT και PETM μας υπενθυμίζουν ότι η αγορά είναι ένα περίπλοκο υφαντό, φτιαγμένο από νήματα στήριξης, αντίστασης και την επιρροή της ακολουθίας Fibonacci. Μαθαίνοντας να διαβάζουμε αυτά τα μοτίβα, μπορούμε να πλοηγηθούμε στις διακυμάνσεις της αγοράς με μεγαλύτερη αυτοπεποίθηση.
Χρυσές διορθώσεις
Στον κόσμο των χρηματοοικονομικών αγορών, οι τιμές συχνά βρίσκουν στήριξη ή αντίσταση σε συγκεκριμένα επίπεδα, γνωστά ως επίπεδα διόρθωσης Fibonacci, ιδιαίτερα γύρω από το 61.8% και το 62%. Αυτά τα επίπεδα δρουν ως αόρατα σημεία αντίστασης και στήριξης, όπου οι αγοραστές και οι πωλητές συγκεντρώνουν τη δραστηριότητά τους.
Ας δούμε δύο παραδείγματα που δείχνουν πώς λειτουργούν αυτά τα επίπεδα Fibonacci.
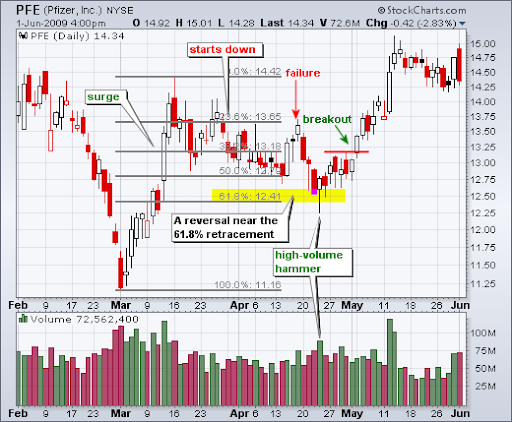)
Αρχικά, ας μιλήσουμε για την Pfizer (PFE). Μετά από μια περίοδο πτώσης των τιμών, η PFE βρήκε σημείο στήριξης κοντά στο επίπεδο διόρθωσης 62%.
Πριν από αυτήν την επιτυχημένη ανάκαμψη, η PFE προσπάθησε να βρει στήριξη στο επίπεδο 50%, αλλά απέτυχε. Μόνο όταν εμφανίστηκε ένα bullish "hammer" candlestick pattern με υψηλό όγκο συναλλαγών, ξεκίνησε η πραγματική αντιστροφή της τάσης.
Λίγο αργότερα, η PFE έσπασε την αντίσταση και κινήθηκε σε ακομα υψηλότερα επίπεδα τιμών.
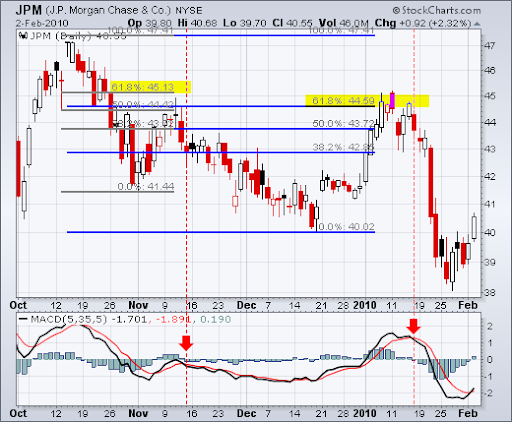)
Αντίθετα, η JP Morgan (JPM) βίωσε μια διαφορετική εξέλιξη. Μετά από μια ισχυρή ανοδική πορεία, η JPM έφτασε στο επίπεδο 62% Fibonacci και στη συνέχεια αντιμετώπισε ισχυρή αντίσταση.
Ο δείκτης MACD, ο οποίος βοηθά στον εντοπισμό αλλαγών στην τάση, γύρισε προς τα κάτω, σηματοδοτώντας μια πιθανή αντιστροφή. Ένα κόκκινο πτωτικό candlestick και ένα gap προς τα κάτω επιβεβαίωσαν την αντίσταση στο 62%.
Παρά την προσωρινή προσπάθεια για ανάκαμψη, η JPM τελικά υπέκυψε στην καθοδική πίεση.
Περιορισμοί στη χρήση των επιπέδων διόρθωσης Fibonacci
Υπάρχουν αρκετές σημαντικές πτυχές που πρέπει να γνωρίζετε κατά την εφαρμογή των επιπέδων διόρθωσης Fibonacci.
Μία από τις βασικές κριτικές είναι ότι, με τόσες πολλές αναλογίες Fibonacci διαθέσιμες, οι τιμές τείνουν να αντιστρέφονται κοντά σε κάποια από αυτές, ακόμα και τυχαία. Η μεγαλύτερη πρόκληση είναι ο καθορισμός της αναλογίας που θα έχει πραγματική σημασία για κάθε συγκεκριμένη κίνηση της τιμής.
Αν μια συναλλαγή δεν αποδώσει με βάση μια συγκεκριμένη αναλογία, οι traders μπορούν πάντα να ισχυριστούν ότι έπρεπε να χρησιμοποιήσουν μια διαφορετική.
Τα μαθηματικά είναι ακριβή, αλλά η εφαρμογή των επιπέδων Fibonacci στις απρόβλεπτες αγορές είναι περισσότερο τέχνη παρά επιστήμη. Συνήθως απαιτείται μια επιπλέον τεχνική επιβεβαίωση πέρα από τους ίδιους τους αριθμούς Fibonacci. Η σωστή διαχείριση κινδύνου παραμένει ζωτικής σημασίας κατά τη χρήση των επιπέδων διόρθωσης Fibonacci.
Συμπέρασμα
Συνοψίζοντας, τα επίπεδα διόρθωσης Fibonacci μπορούν να αποτελέσουν ένα αποτελεσματικό εργαλείο για τον καθορισμό πιθανών περιοχών διόρθωσης, εντοπίζοντας τα επίπεδα στήριξης και αντίστασης.
Παρατηρώντας τα βασικά επίπεδα 23.6%, 38.2% και 61.8%, οι traders μπορούν να κατανοήσουν την ψυχολογία της αγοράς και να προσαρμοστούν σε αυτήν.
Ωστόσο, απαιτείται προσοχή, καθώς τα επίπεδα Fibonacci θα πρέπει να χρησιμοποιούνται σε συνδυασμό με άλλους τεχνικούς δείκτες ανάλυσης, καθώς και με τη θεμελιώδη ανάλυση, για πιο αξιόπιστα αποτελέσματα.
Συχνές ερωτήσεις (FAQs)
Πώς επιλέγετε τα επίπεδα Fibonacci;
Τα επίπεδα Fibonacci είναι ενσωματωμένα στο εργαλείο διόρθωσης Fibonacci. Τα επίπεδα 38.2% και 61.8% θεωρούνται τα πιο σημαντικά.
Τι είναι οι "ζώνες συναγερμού" στις διορθώσεις Fibonacci;
Οι "ζώνες συναγερμού" στις διορθώσεις Fibonacci είναι τα βασικά επίπεδα (38.2%, 50% και 61.8%) όπου είναι πιθανό να συμβούν αναστροφές τιμών. Οι traders παρακολουθούν στενά αυτά τα επίπεδα για πιθανά σήματα συνέχισης ή αντιστροφής της τάσης.
Ποια είναι η στρατηγική Fibonacci;
Η πιο κοινή στρατηγική Fibonacci είναι η χρήση των επιπέδων ως σημεία εισόδου, η μερική λήψη κερδών, ή η πλήρης έξοδος από θέσεις όταν η τιμή φτάνει σε ένα από τα βασικά επίπεδα.
Πώς μπορούν να χρησιμοποιηθούν οι διορθώσεις Fibonacci στο εμποριο;
Οι διορθώσεις Fibonacci μπορούν να χρησιμοποιηθούν ως σημεία εισόδου ή ως επίπεδα για τη μερική ή πλήρη λήψη κερδών.
Πώς μπορούν να συνδυαστούν οι διορθώσεις Fibonacci με αλλους δείκτες;
Τα επίπεδα διόρθωσης Fibonacci μπορούν να συνδυαστούν με κινητούς μέσους όρους (MA ή SMA), Bollinger Bands, MACD καθως και άλλους τεχνικούς δείκτες. Όσο περισσότερες επιβεβαιώσεις υπάρχουν από διαφορετικούς δείκτες, τόσο μεγαλύτερη είναι η πιθανότητα μιας επιτυχημένης συναλλαγής.

