Cocoa Price Prediction: Expert Analysis Reveals Market Trends 2026–2030

Table of Contents
Current State of the Global Cocoa Market 2026
Historic Price Analysis and Current Market Positioning
Cocoa Price Prediction in the Next 2027–2030
Key Factors Driving Cocoa Price Fluctuations
Frequently Asked Questions
The cocoa market has entered a period of exceptional volatility, placing cocoa price prediction at the center of attention across global commodity markets. After an unprecedented price cycle, cocoa prices in 2026 are being shaped by shifting market trends, tight supply conditions, and heightened sensitivity within futures contracts traded on major exchanges. This cocoa price analysis combines historical patterns, current market positioning, and long-term forecasting to assess how cocoa prices may evolve from 2026 through 2030, offering insight into both short-term dynamics and structural changes shaping the market ahead.
Key Takeaways
- Short-term outlook (2026). Cocoa prices in 2026 are projected to trade mostly in the USD 5,500–7,000 per metric ton range, according to WalletInvestor, reflecting ongoing supply tightness, low inventories, and elevated market volatility.
- Price stabilization at higher levels. Market trends indicate consolidation after the 2024–2025 price shock, with cocoa unlikely to return to its historical USD 2,000–3,000 trading range.
- Futures-led price discovery. ICE cocoa futures remain the primary mechanism for price formation, rapidly incorporating changes in crop forecasts, export flows, currency movements, and speculative positioning.
- Long-term price expectations (2027–2030). WalletInvestor forecasts structurally higher prices, with cocoa potentially reaching USD 8,900 by end-2027, USD 10,800 in 2028, USD 12,700 in 2029, and above USD 14,500 by 2030.
- Weather and geographic concentration. Heavy reliance on West Africa, which accounts for roughly 70% of global supply, increases price sensitivity to droughts, excessive rainfall, and climate variability in Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana.
- Geopolitics, sanctions, and trade policy. Sanctions, export controls, EU sustainability regulations, and potential trade tariffs add cost pressure and risk premiums, supporting higher cocoa prices.
- Overall market expectation. The prevailing outlook favors sustained price strength with continued volatility, rather than a cyclical return to past lows.
Current State of the Global Cocoa Market 2026
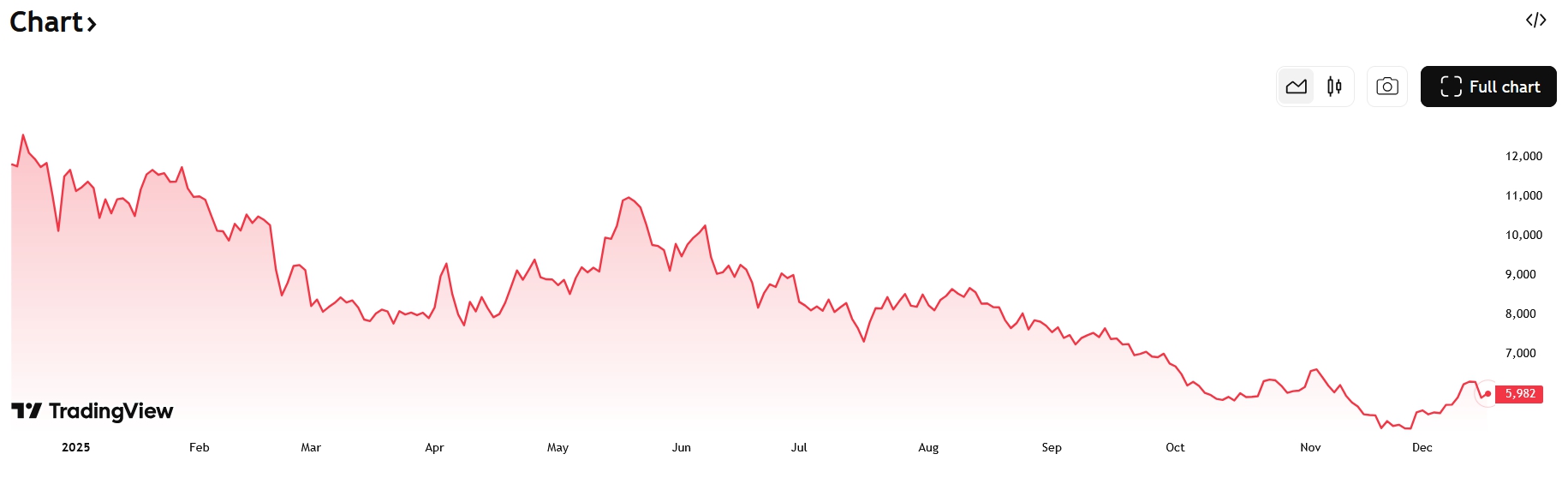
Entering 2026, the global cocoa market remains under intense scrutiny after one of the most extreme price cycles in its modern history. As of December 16, 2025, price discovery continues to be led by cocoa futures traded on the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE), which function as the global benchmark for both physical cocoa pricing and risk management. ICE New York cocoa futures, quoted in US dollars per metric tonne, are consolidating in the USD 5,800–6,000 range, while London ICE contracts, denominated in pounds sterling, follow a similar directional pattern. Together, these instruments define prevailing cocoa price trends and anchor expectations for the year ahead.
Following the historic rally seen earlier in 2025, cocoa prices have entered a corrective phase. However, this adjustment should not be interpreted as a full reversal. Instead, the dominant market trend suggests a transition toward a higher structural price range, reflecting the market’s reassessment of long-term supply resilience. Since cocoa price is measured in futures contracts, movements on ICE offer a clear, real-time reflection of global cocoa market conditions and shifting trader sentiment.
Several interconnected market trends are currently shaping cocoa pricing dynamics and are central to any credible cocoa price forecast for 2026:
- Post-Peak Price Stabilization. After extreme highs, cocoa futures have stabilized rather than collapsed. This trend reflects a balance between reduced speculative enthusiasm and persistent physical tightness, keeping prices well above historical averages.
- Ongoing Structural Tightness in the Global Cocoa Market. Although weather expectations in key producing regions have improved, global inventories remain thin. ICE-monitored stock levels signal limited buffer capacity, meaning the market remains highly exposed to even minor supply disruptions.
- Elevated Volatility in Cocoa Futures Trading. Price action on the Intercontinental Exchange shows heightened sensitivity to crop estimates, export flows, and currency movements. This underscores a market trend where short-term information flow increasingly drives futures pricing.
- Demand Adjustment at High Price Levels. Elevated cocoa prices have begun to affect downstream demand. Chocolate manufacturers are adjusting formulations and procurement strategies, which feeds back into cocoa market conditions by moderating spot demand without eliminating it.
Together, these factors illustrate a cocoa market that is no longer driven purely by panic buying, yet remains structurally tight. The market trend continues to impact cocoa price primarily through futures-led price discovery, reinforcing the importance of ICE as the core pricing venue. Futures contracts traded on the commodity market now reflect a cautious equilibrium between supply risk and demand adaptation.
Cocoa Futures on ICE: Price Trends Over the Past 12 Months
In summary, cocoa market conditions at the start of 2026 can be described as tight but stabilizing. Prices remain volatile, inventories constrained, and market participants highly reactive to new information. This environment forms a critical foundation for forward-looking analysis, as future cocoa price forecasts will depend on whether these prevailing market trends persist or begin to unwind in the years ahead.
Historic Price Analysis and Current Market Positioning
Understanding the current cocoa price level requires placing it within a broader framework of commodity cycles and long-term historical price analysis. Technical analysis of historical price patterns reveals recurring support and resistance levels that inform forward-looking price predictions. The multi-decade uptrend that began around 2000-2001 has established a diagonal support line tested successfully in 2000, 2004, and 2013, while the December 2024 high of $12,931 per ton now serves as critical resistance.
Current technical support zones are identified at approximately $5,465-$5,521 per ton, representing key pivot points where buying interest historically intensifies. Over the past fifteen years, cocoa prices have repeatedly moved through pronounced boom-and-bust phases driven by supply shocks, demand elasticity, and shifts in speculative activity. These recurring cycles highlight the role of price volatility as a defining feature of the cocoa market rather than an exception.
From 2010 to 2023, cocoa prices generally traded within a relatively stable range, punctuated by episodic spikes linked to weather disruptions or political instability in major producing regions. The 2024–2025 rally marked a clear break from this pattern, pushing prices far above previous cyclical highs. This deviation signals a change in market positioning, with cocoa transitioning from a historically range-bound commodity into one characterized by structurally higher price expectations.
To illustrate how this structural shift has translated into actual market behavior, the table below summarizes monthly cocoa futures price dynamics over the most recent period, highlighting the scale, speed, and volatility of the post-peak correction.
| Date |
Price |
Open |
High |
Low |
Trading Volume |
| Jan 01, 2026 |
4,995.00 |
5,943.50 |
6,273.50 |
4,857.00 |
194.67K |
| Dec 01, 2025 |
6,065.00 |
5,456.00 |
6,345.00 |
5,401.00 |
110.26K |
| Nov 01, 2025 |
5,404.00 |
6,174.00 |
6,627.00 |
4,914.00 |
115.78K |
| Oct 01, 2025 |
6,151.00 |
6,731.00 |
6,821.00 |
5,631.00 |
230.31K |
| Sep 01, 2025 |
6,749.00 |
7,420.00 |
7,644.00 |
6,682.00 |
97.05K |
| Aug 01, 2025 |
7,710.00 |
7,750.00 |
8,823.00 |
7,319.00 |
230.60K |
| Jul 01, 2025 |
8,506.00 |
9,165.00 |
9,165.00 |
7,208.00 |
105.40K |
| Jun 01, 2025 |
9,356.00 |
9,625.00 |
10,531.00 |
8,295.00 |
92.53K |
| May 01, 2025 |
9,220.00 |
8,849.00 |
10,677.00 |
8,445.00 |
160.03K |
| Apr 01, 2025 |
9,127.00 |
7,998.00 |
9,652.00 |
7,656.00 |
110.78K |
| Mar 01, 2025 |
7,888.00 |
8,946.00 |
8,954.00 |
7,701.00 |
145.89K |
| Feb 01, 2025 |
9,014.00 |
11,020.00 |
11,324.00 |
8,390.00 |
74.68K |
| Jan 01, 2025 |
10,855.00 |
10,950.00 |
11,574.00 |
9,861.00 |
138.59K |
| Dec 01, 2024 |
11,675.00 |
9,197.00 |
12,931.00 |
8,833.00 |
129.18K |
| Nov 01, 2024 |
9,425.00 |
6,890.00 |
9,520.00 |
6,606.00 |
253.92K |
| Oct 01, 2024 |
7,338.50 |
7,723.00 |
8,169.50 |
6,435.50 |
— |
| Sep 01, 2024 |
7,735.00 |
7,559.00 |
10,116.00 |
6,831.00 |
97.37K |
| Aug 01, 2024 |
7,671.00 |
6,927.00 |
8,242.00 |
6,349.00 |
261.22K |
| Jul 01, 2024 |
6,991.00 |
6,360.00 |
7,562.00 |
6,000.00 |
120.92K |
| Jun 01, 2024 |
6,591.00 |
7,713.00 |
9,004.00 |
6,058.00 |
110.80K |
| May 01, 2024 |
8,586.00 |
9,283.00 |
9,487.00 |
6,418.00 |
223.57K |
| Apr 01, 2024 |
9,283.00 |
9,303.00 |
11,722.00 |
7,756.00 |
338.23K |
| Mar 01, 2024 |
9,766.00 |
6,120.00 |
10,075.50 |
6,093.00 |
17.95K |
| Feb 01, 2024 |
6,510.00 |
4,832.00 |
6,929.00 |
4,828.00 |
328.13K |
Source: Investing.com (15.01.2026)
The monthly data underscores a clear shift in price dynamics between 2024 and 2025. Cocoa futures reached their peak at the beginning of 2025, with January marking the highest price level of the year, before entering a sustained downward trajectory. By contrast, the comparison between year-end periods is particularly revealing: while December 2024 recorded an extreme high near USD 13,000 per ton amid acute supply tightness and speculative positioning, December 2025 prices peaked at just over USD 6,300 per ton. This sharp contraction reflects the unwinding of the 2024 supply-driven risk premium, improved crop expectations, and a normalization of market positioning following the exceptional volatility of the prior year.
The table below places the current market cycle in historical context, comparing key price levels and prevailing market conditions across multiple cocoa price cycles. It illustrates how volatility tends to expand during late-cycle phases, amplifying price movements and reshaping long-term market expectations.
Cocoa Price Cycles: Historical Comparison
| Market Cycle |
Approx. Period |
Price Range (USD/ton) |
Dominant Market Conditions |
| Post-crisis recovery |
2010–2012 |
2,800 – 3,600 |
Supply normalization, demand recovery |
| Mid-cycle stabilization |
2016–2018 |
1,900 – 2,600 |
Oversupply, subdued volatility |
| Pre-rally tightening |
2020–2022 |
2,300 – 3,400 |
Weather risks, rising costs |
| Current cycle |
2024–2026 |
5,800 – 12,000 |
Supply shock, extreme price volatility |
This historical price analysis suggests that today’s cocoa market is positioned in the later stages of an expansionary cycle, where volatility remains elevated and prices are highly sensitive to incremental changes in supply or demand.
Cocoa Price Prediction in the Next 2027–2030
Long-term price prediction for cocoa between 2027 and 2030 requires a scenario-based approach, as uncertainty increases with longer forecasting horizons. Most analyst predictions converge on the view that cocoa is entering a structurally tighter phase, shaped by chronic supply constraints, rising production costs, and evolving demand patterns. Forecasts from Trading Economics and major financial institutions such as J.P. Morgan point toward sustained price strength rather than a return to historical lows.
Alternative forecasting platforms such as WalletInvestor provide algorithmically-driven price projections that complement institutional analyst views, with their models projecting cocoa to reach approximately $9,450 per ton within 12 months and potentially $18,225 by 2030. These algorithmic forecasts, generated through machine learning and technical analysis, offer additional perspective on potential price trajectories based on historical patterns and momentum indicators.
The dominant assumption underlying these price forecasts is that global cocoa supply growth will struggle to keep pace with demand over the medium term. Aging plantations, climate-related yield risks, and limited scope for rapid acreage expansion continue to constrain output. At the same time, consumption growth is expected to remain positive, even if higher prices temper demand growth at the margins. Together, these forces define a market trend favoring elevated prices with persistent volatility.
While near-term fluctuations are inevitable, long-range forecasts suggest a gradual upward trajectory for cocoa prices, with year-over-year gains reflecting both inflationary pressures and structural scarcity. The table below summarizes projected cocoa price levels for the 2027–2030 period, expressed in US dollars per metric ton.
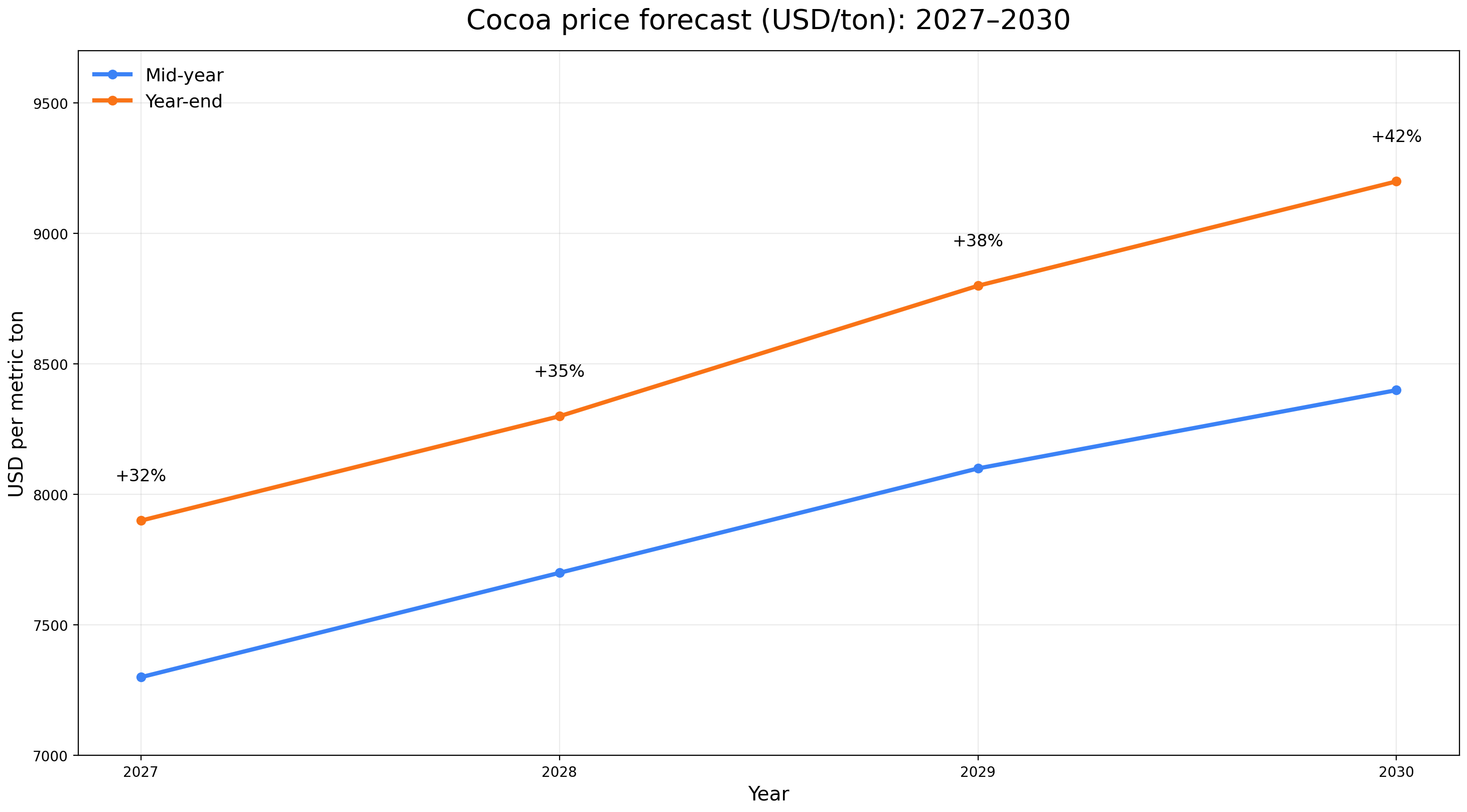
Cocoa Price Forecasts: 2027–2030
| Year |
Mid-Year Estimate |
Year-End Estimate |
YoY Change (Year-End) |
| 2027 |
7,300 |
7,900 |
+32% |
| 2028 |
7,700 |
8,300 |
+35% |
| 2029 |
8,100 |
8,800 |
+38% |
| 2030 |
8,400 |
9,200 |
+42% |
Sources: WalletInvestor, Trading Economics, J.P. Morgan
To complement the long-term projections above, the following sections provide a more granular, year-by-year breakdown of cocoa price forecasts from 2027 through 2030. Each subsection presents monthly price estimates, offering insight into expected intra-year dynamics, trend consistency, and volatility patterns across the extended forecast horizon.
 Cocoa Price Outlook
Cocoa Price Outlook
Cocoa Price Forecast for 2027
The 2027 outlook suggests a gradual upward trend over the course of the year, with prices starting near the USD 7,000 per ton level and advancing toward the upper USD 8,000 range by year-end. This pattern implies sustained market tightness and continued pricing power, while the relatively smooth monthly progression points to a stabilization phase following the extreme volatility observed in 2024–2025.
| Date |
Opening price |
Closing price |
Minimum price |
Maximum price |
| January 2027 |
7,016.461 |
7,410.264 |
7,016.461 |
7,411.946 |
| February 2027 |
7,420.145 |
7,496.821 |
7,420.145 |
7,505.803 |
| March 2027 |
7,491.497 |
7,706.340 |
7,491.497 |
7,706.340 |
| April 2027 |
7,730.543 |
7,971.434 |
7,729.533 |
7,982.798 |
| May 2027 |
7,953.370 |
8,077.221 |
7,933.230 |
8,077.221 |
| June 2027 |
8,103.876 |
8,117.849 |
8,103.876 |
8,186.463 |
| July 2027 |
8,132.868 |
8,223.517 |
8,119.903 |
8,234.506 |
| August 2027 |
8,212.574 |
8,357.077 |
8,212.574 |
8,357.077 |
| September 2027 |
8,356.627 |
8,427.768 |
8,354.694 |
8,432.639 |
| October 2027 |
8,413.351 |
8,464.102 |
8,366.014 |
8,467.936 |
| November 2027 |
8,470.896 |
8,681.693 |
8,470.896 |
8,681.693 |
| December 2027 |
8,696.011 |
8,908.930 |
8,696.011 |
8,917.224 |
Sources: WalletInvestor (15.01.2026)
Cocoa Price Forecast for 2028
The 2028 outlook points to a continuation of the upward price trend, with cocoa futures gradually moving into the USD 10,000 per ton range during the second half of the year. Monthly projections indicate steady appreciation rather than abrupt spikes, suggesting that prices are increasingly driven by structural supply constraints and long-term demand factors rather than short-term speculative distortions.
| Date |
Opening price |
Closing price |
Minimum price |
Maximum price |
| January 2028 |
8,911.300 |
9,309.141 |
8,911.300 |
9,309.141 |
| February 2028 |
9,330.746 |
9,402.994 |
9,330.746 |
9,402.994 |
| March 2028 |
9,403.936 |
9,614.477 |
9,403.936 |
9,615.790 |
| April 2028 |
9,632.384 |
9,869.152 |
9,632.384 |
9,879.447 |
| May 2028 |
9,853.756 |
9,996.494 |
9,829.522 |
9,996.494 |
| June 2028 |
10,022.42 |
10,019.04 |
10,006.67 |
10,080.36 |
| July 2028 |
10,012.66 |
10,108.91 |
10,012.66 |
10,132.06 |
| August 2028 |
10,124.49 |
10,268.13 |
10,123.84 |
10,268.13 |
| September 2028 |
10,258.48 |
10,314.95 |
10,250.05 |
10,328.77 |
| October 2028 |
10,291.29 |
10,381.61 |
10,266.69 |
10,381.61 |
| November 2028 |
10,385.40 |
10,603.79 |
10,385.40 |
10,603.79 |
| December 2028 |
10,609.17 |
10,803.10 |
10,609.17 |
10,812.60 |
Sources: WalletInvestor (15.01.2026)
Cocoa Price Forecast for 2029
By 2029, cocoa prices are projected to enter a more advanced stage of the upcycle, with monthly forecasts indicating a steady climb toward the USD 12,000–12,700 per ton range by year-end. The pace of appreciation appears more measured, pointing to a market that is adjusting to persistently high price levels while continuing to reflect long-term supply limitations and structurally firm demand.
| Date |
Opening price |
Closing price |
Minimum price |
Maximum price |
| January 2029 |
10,801.14 |
11,224.66 |
10,801.14 |
11,224.66 |
| February 2029 |
11,245.31 |
11,297.87 |
11,239.18 |
11,297.87 |
| March 2029 |
11,315.07 |
11,499.80 |
11,304.71 |
11,501.42 |
| April 2029 |
11,516.81 |
11,753.15 |
11,516.81 |
11,774.69 |
| May 2029 |
11,766.42 |
11,905.39 |
11,725.46 |
11,905.39 |
| June 2029 |
11,906.00 |
11,916.15 |
11,906.00 |
11,982.02 |
| July 2029 |
11,906.56 |
12,020.94 |
11,906.56 |
12,029.65 |
| August 2029 |
12,019.79 |
12,154.18 |
12,019.79 |
12,163.72 |
| September 2029 |
12,145.64 |
12,215.79 |
12,145.64 |
12,228.94 |
| October 2029 |
12,193.69 |
12,275.66 |
12,162.35 |
12,275.66 |
| November 2029 |
12,295.89 |
12,486.13 |
12,289.78 |
12,486.13 |
| December 2029 |
12,522.81 |
12,692.88 |
12,522.81 |
12,709.77 |
Sources: WalletInvestor (15.01.2026)
Cocoa Price Forecast for 2030
The 2030 projections suggest a phase of consolidation at elevated price levels, with cocoa futures largely stabilizing within the USD 13,000–14,600 per ton range over the course of the year. Rather than signaling renewed acceleration, this pattern reflects market adaptation to structurally tighter supply conditions, where higher prices become embedded in the long-term equilibrium of the cocoa market.
| Date |
Opening price |
Closing price |
Minimum price |
Maximum price |
| January 2030 |
12,712.03 |
13,134.83 |
12,712.03 |
13,134.83 |
| February 2030 |
13,130.23 |
13,209.07 |
13,130.23 |
13,209.07 |
| March 2030 |
13,200.75 |
13,385.50 |
13,197.57 |
13,387.42 |
| April 2030 |
13,401.61 |
13,665.59 |
13,401.61 |
13,668.47 |
| May 2030 |
13,662.40 |
13,788.80 |
13,622.97 |
13,788.80 |
| June 2030 |
13,809.48 |
13,814.67 |
13,809.48 |
13,882.49 |
| July 2030 |
13,801.74 |
13,916.36 |
13,801.74 |
13,927.08 |
| August 2030 |
13,931.43 |
14,049.73 |
13,914.59 |
14,059.06 |
| September 2030 |
14,041.34 |
14,095.54 |
14,041.34 |
14,128.19 |
| October 2030 |
14,106.80 |
14,185.99 |
14,058.69 |
14,185.99 |
| November 2030 |
14,180.89 |
14,363.61 |
14,180.89 |
14,363.61 |
| December 2030 |
14,399.61 |
14,604.14 |
14,399.61 |
14,606.89 |
Sources: WalletInvestor (15.01.2026)
As forecast horizons extend, uncertainty widens, and outcomes become increasingly sensitive to macroeconomic conditions and policy responses. Nonetheless, current projections indicate that cocoa price levels through 2030 are likely to remain well above long-term averages, reinforcing the view that recent market shifts represent a structural change rather than a temporary anomaly.
Key Factors Driving Cocoa Price Fluctuations
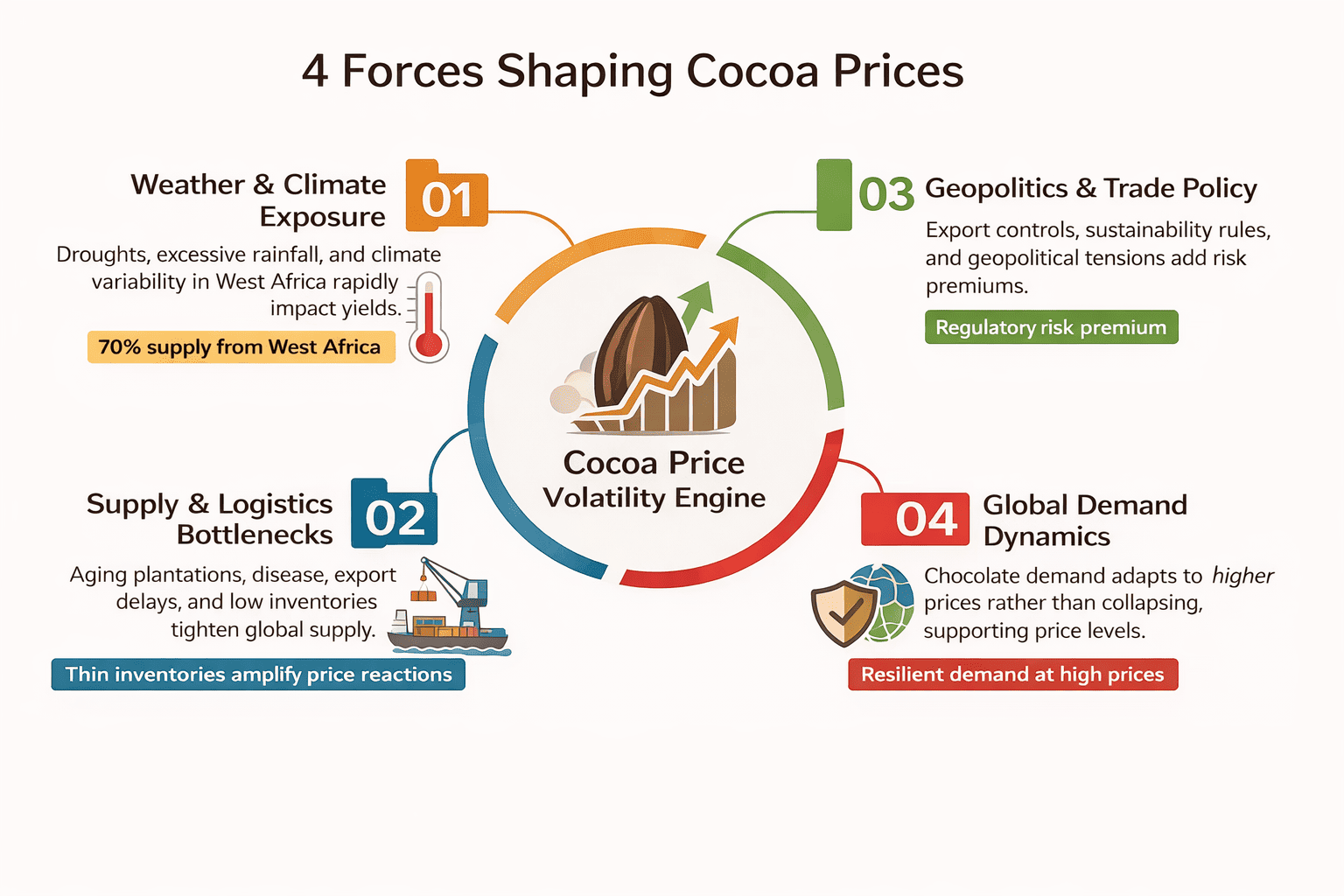
Cocoa price dynamics are shaped by a tightly linked set of fundamental forces, with the cocoa bean at the center of the system. Its biological sensitivity, long production cycle, and geographic concentration make cocoa prices especially responsive to external shocks across global commodity markets. As a result, the main cocoa price drivers tend to reinforce one another rather than act independently.
- Weather conditions and climate exposure. Cocoa cultivation requires stable temperatures of roughly 21–28°C and high humidity, limiting production to equatorial regions such as West Africa, Brazil, and Ecuador. Weather disruptions, including droughts or excessive rainfall in the Ivory Coast and Ghana, can rapidly reduce yields, as seen during the 2023–2024 period, contributing to the sharp price surge into late 2024.
- Supply chain and logistical constraints. Even when harvest volumes are adequate, infrastructure limitations and export delays in producing countries can restrict near-term supply. These bottlenecks often amplify price reactions during periods of market stress by tightening available inventories.
- Geopolitical and regulatory factors. Export policies, pricing mechanisms, and regulatory interventions in producing regions directly influence global cocoa flows. In 2024, rising geopolitical tensions and new trade and regulatory constraints coincided with a notable increase in risk premiums, reinforcing the price spike observed at year-end.
- Demand resilience. Global demand for cocoa products remains relatively stable, with higher prices typically slowing growth rather than causing sharp contractions. This demand resilience allows supply-side shocks to translate more directly into price volatility.
 Factors Driving Cocoa Price
Factors Driving Cocoa Price
Supply Challenges in Major Producing Regions
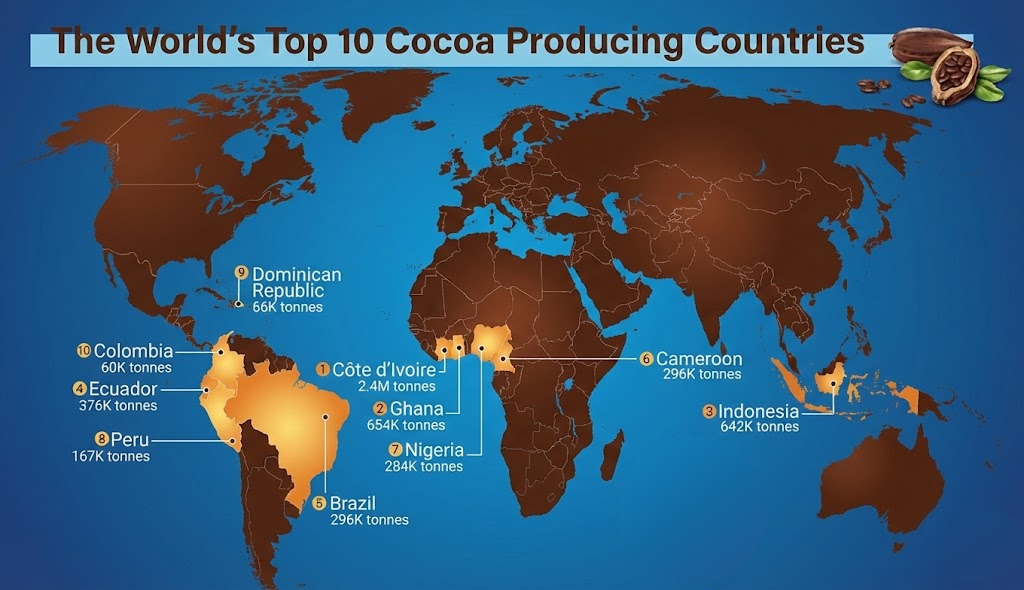
Global cocoa production remains highly concentrated, with West Africa accounting for roughly 70% of total output. Within this region, Côte d’Ivoire (Ivory Coast) supplies about 40% of global cocoa beans, while Ghana contributes close to 20%. This concentration magnifies the impact of regional disruptions on global cocoa prices, as even localized production issues translate rapidly into supply constraints across commodity markets.
Current production data from the International Cocoa Organization reveals the ongoing supply challenges facing the market. The 2024/2025 season shows global cocoa bean production at approximately 4.69 million metric tons, falling short of earlier projections of 4.84 million tons. The current season projects only a modest surplus of 49,000 tonnes—a precarious balance that leaves the market highly vulnerable to weather disruptions or logistical challenges in key producing regions.
The cocoa bean’s biological sensitivity makes production particularly vulnerable to environmental and structural challenges. Aging tree stock, disease pressure, and climate variability continue to limit yield recovery despite supportive price signals. Outside West Africa, countries such as Ecuador play a growing but still secondary role, providing diversification rather than full risk mitigation.
Key regional supply challenges shaping expected global output include:
- Côte d’Ivoire (Ivory Coast): Climate stress and aging plantations. Irregular rainfall patterns and rising temperatures reduce flowering consistency, while a high proportion of old trees constrains productivity despite high prices.
- Ghana: Disease pressure and input shortages. Cocoa swollen shoot virus and limited access to fertilizers continue to suppress yields, affecting both volume and bean quality.
- West Africa overall: Structural production limits. Labor shortages, rising production costs, and regulatory controls slow expansion even when market incentives are strong.
- Brazil: Gradual recovery with structural constraints. Brazil benefits from suitable climate conditions in Bahia and Pará and ongoing rehabilitation of plantations, but production growth remains gradual due to past disease impacts and investment requirements.
- Ecuador: Expansion with constraints. Improved genetics support growth, but infrastructure and scale limitations prevent Ecuador from offsetting West African shortfalls.
- Caribbean region: Niche production profile. Countries such as the Dominican Republic and Trinidad and Tobago contribute high-quality cocoa, but small acreage and fragmented production limit their influence on global supply balances.
- South and Southeast Asia: Emerging but constrained supply. Indonesia and neighboring producers face yield challenges linked to aging trees and competition for land, allowing the region to play a supplementary rather than stabilizing role in global cocoa markets.
Collectively, these factors cap global cocoa bean output, reinforcing supply-driven price volatility.
Leading Cocoa-Producing Countries by Output
| Country |
Cocoa Bean Production, 2023 (metric tons) |
| Ivory Coast |
2,377,442 |
| Ghana |
653,700 |
| Indonesia |
641,741 |
| Ecuador |
375,719 |
| Brazil |
296,145 |
| Cameroon |
295,819 |
| Nigeria |
284,232 |
| Peru |
166,709 |
| Dominican Republic |
65,930 |
| Colombia |
59,831 |
| Papua New Guinea |
43,200 |
| DR Congo |
35,000 |
| Uganda |
35,000 |
| India |
30,000 |
| Venezuela |
29,359 |
Source: Worldpopulationreview
Cocoa-Producing Countries
Demand Dynamics and Economic Influences
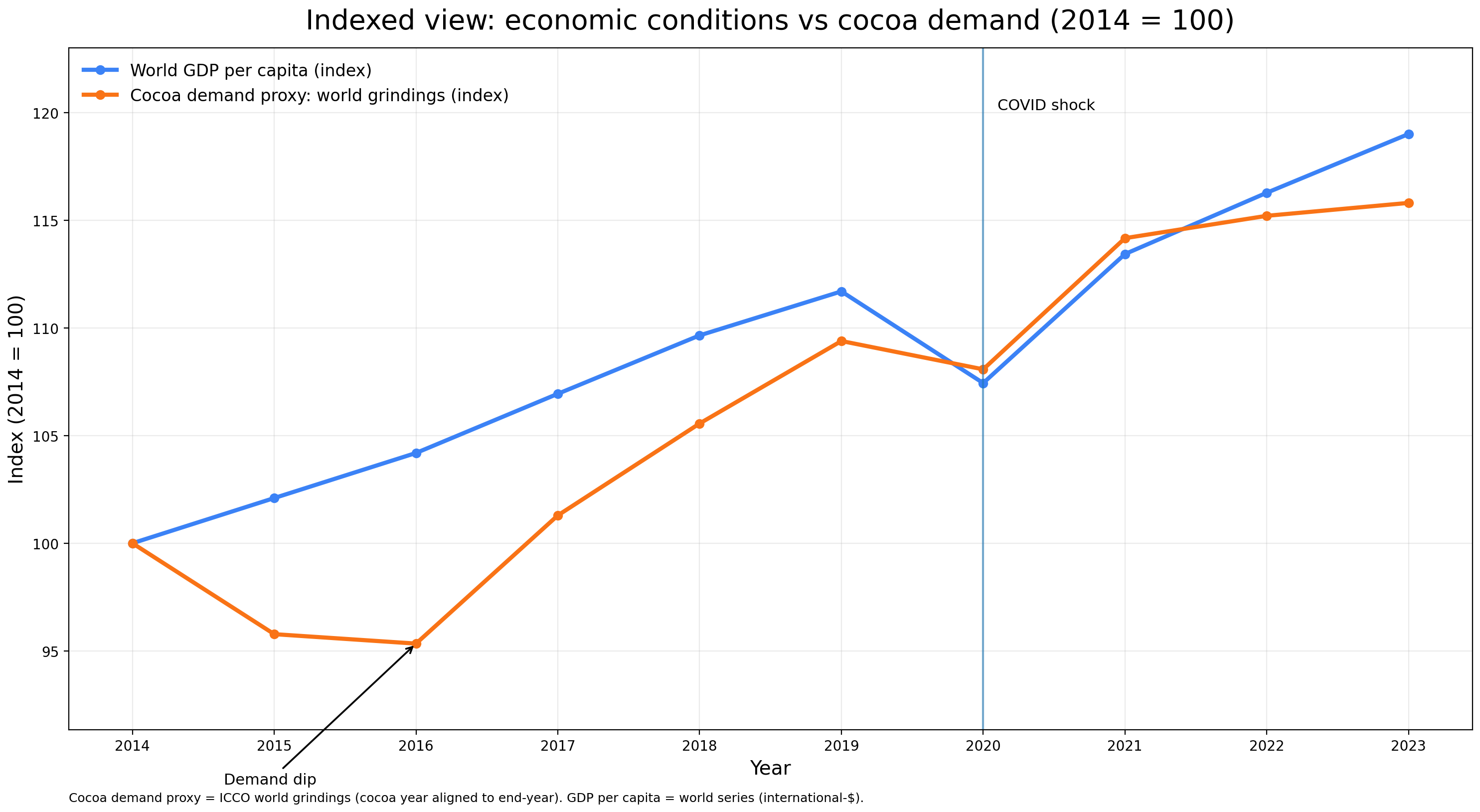
On the demand side, cocoa price movements are shaped by evolving consumer preferences, broader economic conditions, and structural changes within the confectionery industry. Chocolate consumption has historically shown resilience, with sustained price increases tending to reshape demand patterns rather than eliminate demand altogether.
Global consumption resilience is largely supported by the pricing power and brand strength of major confectionery producers. Multinational companies in Europe and North America dominate mass-market volumes, with players such as Mars, Mondelez International, Nestlé, and Ferrero able to absorb and gradually pass through higher cocoa costs. At the same time, premium and specialty brands — including Lindt & Sprüngli, Godiva, and Hershey’s premium lines — play a growing role in Asia and other emerging markets, where consumers show a higher tolerance for price increases. This brand segmentation allows higher cocoa costs to be passed through unevenly across regions. As a result, producers increasingly adjust product formats through smaller portion sizes, recipe reformulation, and a stronger emphasis on higher-margin premium offerings.
Seasonality further amplifies these dynamics, with demand peaking around key consumption periods such as Easter, Christmas, and major gifting seasons, particularly in Europe and North America. During these periods, demand tends to be less price-sensitive, reinforcing short-term price support even amid broader economic pressure. Consequently, cocoa demand adapts across product categories and calendar cycles rather than experiencing abrupt contractions.
Economic conditions influence cocoa demand indirectly through disposable income trends, inflation dynamics, and trade policy developments. During periods of economic stress, mass-market chocolate consumption tends to slow, while premium and specialty segments remain comparatively stable due to stronger brand loyalty and pricing flexibility. In addition, trade restrictions, sanctions, and changes in import or export tariffs can distort regional price transmission by increasing costs for processors and manufacturers or disrupting established supply chains. These combined forces result in a differentiated demand response rather than a uniform contraction, with the prevailing market trend reflecting demand adjustment rather than demand collapse.
Sustainability considerations are also reshaping demand. Ethical sourcing, traceability, and environmental standards increasingly influence purchasing decisions, encouraging manufacturers to secure long-term supply agreements and accept higher input costs. These shifts reinforce the link between long-term demand expectations and cocoa price stability.
Cocoa Demand vs Global Income
FAQ
-
How high will cocoa prices go in 2026?
According to WalletInvestor projections, cocoa prices in 2026 are expected to peak near USD 7,000 per ton by December, marking the highest level of the year. Monthly forecasts indicate a gradual rise from approximately USD 5,600 in February, with interim highs forming around USD 6,300–6,500 during August and September. The projected year-end maximum reflects persistent supply constraints and elevated production risks embedded in forward pricing.
-
What is the outlook for cocoa in 2026?
The 2026 outlook points to a year of elevated prices marked by alternating advances and pauses rather than a smooth trend. Prices are projected to recover from early-year levels near USD 5,600 in February, climb steadily through spring and summer, and consolidate in the USD 6,500–7,000 range toward year-end. This pattern suggests stabilization after prior shocks, though month-to-month volatility remains pronounced throughout the year.
-
What are the key drivers of cocoa prices?
Key cocoa price drivers include weather patterns affecting yields, supply chain disruptions limiting export flows, geopolitical factors in producing regions, and resilient consumer demand. These forces interact within global commodity markets, amplifying price volatility when supply constraints coincide with steady or only slowly adjusting demand.
-
Could cocoa go up or down in 2027?
Cocoa prices in 2027 may continue to rise but remain vulnerable to shifts in supply and demand. WalletInvestor projects an increase from around USD 7,000 in January to over USD 8,100 by June, peaking near USD 8,700–8,900 in November–December. However, improved harvests or policy shifts could ease prices, while weather shocks may drive further gains. Forecast uncertainty increases later in the year.
-
What historical patterns can help predict cocoa price movements?
Historical price analysis shows that cocoa prices follow recurring commodity cycles characterized by long periods of stability punctuated by sharp spikes. These cycles are often driven by weather shocks and supply disruptions, with price volatility expanding late in the cycle before eventually moderating as production responds. Seasonal patterns also play a role, with prices historically tending to rise between June and August, coinciding with mid-crop harvest updates and heightened market sensitivity.
-
Is cocoa a buy or sell?
As of January 15, 2026, technical indicators suggest a short-term sell bias in cocoa prices. Momentum indicators such as RSI and MACD remain negative, while most short- and medium-term moving averages point lower. At the same time, oversold signals highlight elevated volatility and the potential for sharp reversals, making careful timing and active risk management essential.
-
How do supply constraints impact cocoa prices?
Supply constraints reduce available cocoa beans relative to demand, causing prices to rise rapidly as buyers compete for limited supply. Low inventories, aging plantations, and logistical disruptions amplify this effect, making cocoa prices particularly reactive to even small changes in expected production or export volumes.
-
How do weather conditions affect cocoa price predictions?
Weather conditions play a critical role in cocoa price forecasts due to the crop’s sensitivity to temperature and moisture. Cocoa trees require average temperatures of 21–28°C and consistently high humidity, typically above 70%, conditions found in equatorial regions such as the Ivory Coast, Ghana, Brazil, and Ecuador. Deviations from these norms — droughts, excessive rainfall, or heat stress — raise disease risk and reduce yields, prompting markets to price in supply constraints well ahead of confirmed harvest data.
-
How accurate are algorithmic cocoa price predictions compared to analyst forecasts?
Algorithmic models rely heavily on historical data and trend extrapolation, which can be effective in stable periods but less reliable during structural shifts. Analyst forecasts incorporate qualitative factors such as weather risk and policy changes, often providing better context when cocoa prices are driven by supply constraints.