-
home
>>
-
Optional solutions
Individual Futures Options Solutions
Take advantage of the features of futures options without having to go through complex
mathematical formulas.

We offer several categories of solutions.
Within each category, only a small number of solutions are provided, primarily for the purpose of illustrating ideas. The number of possible option solutions is practically unlimited.
Global rates have risen. Many banks do not pay comparable interest on deposits. To get a good rate on a deposit, it is usually necessary to choose a long term without the possibility of withdrawing the deposit. Many futures brokers do not pay interest on balances or pay a disproportionate rate.
Solution.Certain option solutions provide fixed returns comparable to current market rate.
In this case:
There is a forecast of changes in prices for an asset over a certain horizon. There is a choice of options solutions on how to work out the forecast. But these solutions are not free, but require the payment of option premiums.
Solution.The right combination of the strategies in Solution 1 and the options solutions provide a “free” solution that offsets the payment of option premiums.

There is a forecast of quite strong movement for the day.
Solution.A today's option (with an expiration date today) is purchased in the hope that the forecast will come true. In this case, profits can be achieved that are multiples of the premium spent.
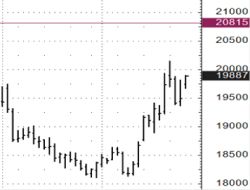
E-Mini S&P 500 futures.
In the area of the top there was a purchase of today's (with expiration today) put with a strike of 4000 for 1.00 points ($50). In the first “poke” down, the option cost 20.00 points ($1,000), that is 20-times of premium paid were made. At the beginning of the second “poke” down, the option cost 34.00 points ($1,700), i.e made 34-times of premium paid.
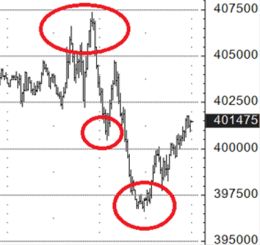

There is an opinion that it is necessary to limit losses by placing stop orders, the so-called “stop loss”. In this case, the stop order may be executed, but the market then turns in the direction of the original position, which, in the end, could even be profitable.
Solution.Using options as an alternative to stop loss. A stop loss implemented in this way gives the position a greater chance of returning to the profitable zone and eliminates losses associated with gaps beyond the stop loss level.
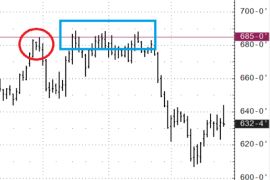
"Stop Loss". Corn futures.
There is a short position in a futures (sold futures). The stop loss level was chosen above the high of 685-0 (red circle). If there was a stop order at 685-0, it would have been triggered (blue area). At the same time, in the end, the market fell and would have brought profit. But the trader was left without a position. Buying a call option with a strike price of 685-0 with sufficient time until expiration would guarantee protection above the 685-0 level, while leaving the position open to profit in the event of a fall. The trade-off for staying in the position is paying an option premium, which would increase losses above the 685-0 level if the market closed above that level on the expiration date.
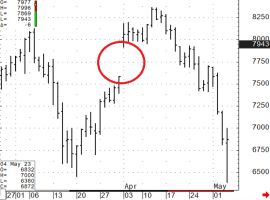
"Gap". Oil futures.
There is a short position in a futures (sold futures). The stop order is at 76.00, limiting potential losses. However, significant news came out over the weekend and the market opened with a “gap” and the stop order was executed at a price of 80.10, realizing additional losses. If, instead of a stop order at 76.00, a call option with a strike price of 76.00 had been purchased, it would have guaranteed the position to be closed at 76.00. In this case, the maximum additional loss would be limited only by the option premium, which would be significantly better compared to an executed stop order at a price of 80.10. Moreover, since using an option as a “stop loss” there is no need to close the position, there was still a chance (if there was enough time before the option expiration) to wait for the fall and realize the profit as a result.

There is a forecast of changes in prices for an asset over a certain horizon. At the same time, you don’t want to lose in the range of current prices.
Solution.Option solutions allow you to achieve break-even or a small profit within a given range of price changes.
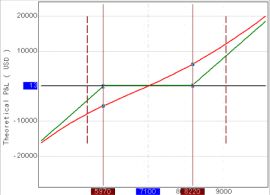
In this case:Oil futures.
Current price 71.00. The forecast period is 3 months. The break-even range is 59.70 and above. If you just buy futures, the break-even range is 71.00 and above.

There is a forecast of levels for the day and the likelihood of their achievement. It is not clear what is the best way to work out this forecast.
Solution.Use of so-called Event contracts on CME, which represent binary options. These are fixed bets with fixed maximum profits and losses.
Futures sul gas naturale.
Previsione: I futures non chiuderanno al di sotto di 2,200 oggi. Si acquista un contratto di questo tipo e si pagano 10,75 dollari. Il pagamento massimo previsto dal contratto è di 20,00 dollari. Se il mercato chiude al di sopra di 2,200, il contratto pagherà 20,00 dollari, il che significa 9,25 dollari di profitto (20,00 ricevuti meno 10,75 dollari pagati).

There is a forecast of changes in prices for an asset over a certain horizon. There is a desire to work out the situation by purchasing an option. Profit on the expiration date is realized only if the asset closes above (if a call is purchased) or below (if a put is purchased) the option strike. And you will need to deduct the premium paid.
Solution.The use of option combinations that allow you not to lose paid premiums in the range from current prices to the strike price. The trade-off is increased losses when prices move from current levels in the opposite direction to the forecast.
Gold Futures.
Forecast: Futures will rise. You can buy a call with a strike of 2060 at a price of 21.50. Moreover, on the expiration date, profitability will be achieved only at a level above 2081.50. Below these levels there will be a loss.
By adding several other options, you can get the following configuration: The price at which losses begin is moved below 1990.00. Trade-off - losses increase below 1990.00 compared to the limited losses of 21.50 points in the situation of just buying a call.
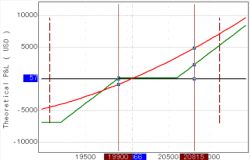

There is a position that is not developing according to plan - it is unprofitable. The position would happily be closed at breakeven, but the market has moved relatively far from the breakeven price. Often traders try to “fight back” using the so-called “averaging”: an additional purchase of an asset in the case of a long losing position or an additional sale of an asset in the case of a short losing position. Thereby bringing the break-even price closer. The problem is that the risk increases in the event of further unfavorable price movements.
Solution.Use of option combinations that allow you to move break-even price closer to current market prices. At the same time, the risk in the event of further unfavorable price movements does not increase.
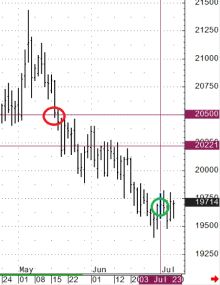
Gold futures.
A long position was opened at 2050.00 (red circle). An option combination has been added at the price (green circle). Which made it possible to reduce the breakeven price to 2022.10 on the options expiration date without increasing the downside risk. Compromise - there is no profit potential above the price of 2022.10.

There is a forecast of the price level for entering a position. But the price may not reach there.
Solution.An option is sold with a strike at the level of the price entry into the position. If the price is outside the strike price on the expiration date, the option is exercised into the futures and a resulting futures position is obtained. At the same time, the opening price was improved by the amount of the option premium received. If the price does not reach the strike level, the premium received from selling the option is retained. Compromise - if the price “moved” beyond the strike and then returned on the expiration date, the option will not be exercised and there will be no futures position.
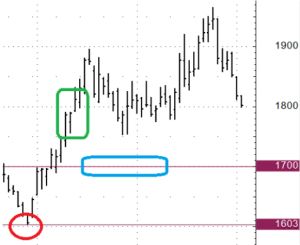
Future sullo zucchero.
Quando i prezzi si trovano nel rettangolo verde, si identifica una tendenza al rialzo. Il punto di ingresso viene determinato al livello del rettangolo blu. Viene venduta una put con strike al livello del rettangolo blu (1700). Se alla data di scadenza il prezzo fosse inferiore a 1700, la put verrebbe eseguita sul future e verrebbe aperta una posizione lunga (acquisto del future) a 1700. In questo caso, il prezzo di acquisto sarebbe migliorato dell'importo del premio ricevuto dalla vendita della put. Nella situazione reale, il mercato non ha raggiunto i livelli dello strike. L'unico profitto è stato il premio della put. Non è così offensivo rispetto alla situazione in cui ci sarebbe un ordine di acquisto di future al livello di 1700. È anche possibile che il prezzo scenda al di sotto dello strike e poi torni al di sopra dello strike alla data di scadenza dell'opzione. In questo caso, non ci sarà alcuna posizione nei futures e si guadagnerà solo il premio.

There are statistical characteristics of the underlying asset (futures). Current characteristics differ from average values. The intention is to try to make money on the current market situation.
Solution.Using options on the underlying asset, a strategy for exploiting the statistical characteristics of the market is built.
The average daily price range for the last month exceeds the daily ranges for the last two days. Short-term options are purchased, which can bring profit if the daily price range increases.

Esiste un'ampia gamma di strategie in opzioni che devono essere gestite in modo dinamico e che possono essere adattate alle esigenze specifiche del trader/investitore.
Per implementare le strategie in opzioni nel tempo è necessaria una sufficiente esperienza con i portafogli di opzioni e una profonda comprensione delle proprietà delle opzioni. Solo specialisti altamente qualificati possono garantire un'esecuzione di alta qualità di tali strategie.
Esiste una strategia di investimento a lungo termine, che prevede anche l'utilizzo di futures. Sono possibili vendite dinamiche tattiche di opzioni su questi futures per ricevere i premi delle opzioni come possibile reddito aggiuntivo.
Soluzione.Si sta sviluppando una strategia individuale che utilizza le opzioni.

Historically, options on some asset classes, especially equity indices, have been overpriced. This implies a possible advantage to selling volatility. But there are subtleties and nuances.
Solution.An individual strategy using options is being developed.

Una volta creata una posizione, la vostra visione del mercato può cambiare.
Soluzione.Le opzioni consentono di modificare dinamicamente la composizione del portafoglio per adattarsi ai cambiamenti del mercato. Allo stesso tempo, non è necessario chiudere completamente il portafoglio iniziale. È sufficiente aprire ulteriori posizioni o modificare quelle esistenti.

Formulate your wishes, including problem areas when trading, and we will try to improve the situation.
